Everything You Need to Know About Insomnia
Everything You Need
to Know About Insomnia
Insomnia is a form of sleep deprivation. Insomniacs have trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or doing both.
TESTING | CHILDREN | ANXIETY | DEPRESSION |
COMPLICATIONS | SUMMARY | CASE STUDIES
Insomnia
When people with insomnia get up from their sleep, they generally don’t feel refreshed. Fatigue and other symptoms may result as a result of this.
According to the British Sleep Society, insomnia is the most frequent of all sleep disorders (BSS).
In fact, according to the BSS, one-third of all individuals experience insomnia symptoms. Approximately 6 to 10% of all individuals have symptoms severe enough to be diagnosed with insomnia disorder.
Insomnia is defined by the BSS as a sleep condition in which persons have difficulty sleeping or staying asleep. If both of these criteria are met, a clinical diagnosis of insomnia is made:
- For a minimum of three months, you must have sleep problems at least three evenings a week.
- Major distress or functional issues in a person’s life are caused by sleep problems.
• Physical pain
• Stress
• Jet lag
• Some medications
• A distressing or traumatic event
• Changes to your sleep habits, like sleeping in a hotel or new home
• Medications that make sleeping difficult, such as arthritis or back pain
• Anxiety or depression, and psychological disorders
• Substance use
• Some medications
• Sleep apnea
• Diabetes
• High stress levels
• Depression or distress caused by a life event are examples of emotional disorders.
• Low income
• Traveling through various time zones
• Sedentary lifestyle
• Alterations in working hours or night shifts
• A habit of waking up too early in the morning
• Sleep that isn’t really refreshing
• Having difficulty falling or staying asleep
• Mood changes
• Fatigue
• Irritability
• Breathing trouble
• Rapid shallow breathing
• Pressure in your chest, heaviness or pain
• Bluish or grey lips, skin, or nail beds
• Rapid heart rate
• Confusion
• Drowsiness
Insomnia can be treated with both pharmacological and nonpharmaceutical methods.
A doctor can advise you on which therapies are best for you. It’s possible that you’ll have to try a few different therapies before discovering the one that works best for you.
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is recommended as a first-line treatment for chronic insomnia in adults by Mind, a UK mental health advice and support charity.
Training in sleep hygiene may also be recommended. Insomnia can be caused by habits that disrupt sleep. Some of these disruptive behaviours can be changed with sleep hygiene training.
Changes that may be suggested include:
- Caffeinated beverages should be avoided near bedtime.
- Avoiding exercise in the hours leading up to bedtime
- Reducing the amount of time you spend in bed when you aren’t sleeping, such as watching TV or surfing the web on your phone
If you have an underlying psychological or medical issue that is causing your insomnia, seeking therapy for it can help you sleep better.
Find out more about insomnia treatments:
for treating Patients suffering from Insomnia
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
for Insomnia
Ozone Therapy for Insomnia
Red Light Therapy
for Insomnia
Infrared Sauna Therapy
for Insomnia
Medications are sometimes used to treat insomnia.
An antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine, is an example of an over-the-counter (OTC) drug that can be used for sleep (Benadryl).
Because OTC medications for insomnia might have side effects, especially if used long term, it’s crucial to consult a doctor before using one.
The following are examples of prescription drugs that can be used to treat insomnia:
- Zolpidem (Lunesta)
- Eszopiclone (Ambien)
Before taking any pills or supplements to cure your insomnia, see your doctor.
There could be serious drug interactions or negative effects. Not all “sleep aids” are suitable for everyone.
Find out more about insomnia drugs.
Many cases of insomnia can be effectively managed by making lifestyle modifications or attempting home treatments.
Warm milk, herbal tea, and valerian root are just a few examples of natural sleep aids.
Meditation is a drug-free, natural, and simple approach to treating insomnia.
Meditation, according to a 2015 study, can improve the quality of your sleep and make it easier to fall and remain asleep.
Meditation, according to the Mayo Clinic, can also help with the symptoms of diseases that can cause insomnia. These are some of them:
- Anxiety
- Stress
- Digestive Problems
- Depression
- Pain
Many apps and videos are available to help you practice meditation.
During the sleep cycle, the hormone melatonin is naturally produced. Melatonin pills are frequently used to help people sleep better.
Melatonin has not been proven to benefit adults with insomnia in studies.
There is some evidence that vitamins can help you fall asleep faster, but further research is needed.
Melatonin is generally considered safe for a short length of time, but its long-term safety has yet to be proven.
If you’re thinking about using melatonin, consult a doctor first.
Essential oils are powerful aromatic liquids derived from a range of sources, including:
- Plants
- Flowers
- Trees
People use essential oils to treat a number of ailments by breathing them or massaging them into their skin. Aromatherapy is the name for this type of treatment.
The following essential oils are thought to aid sleep:
- Roman chamomile
- Cedarwood
- Lavender
- Sandalwood
- Neroli, or bitter orange
Aromatherapy was found to be helpful in improving sleep in a review of 12 trials published in 2015.
Lavender was found to be particularly effective in promoting and maintaining sleep in another investigation. A blend of essential oils reduced sleep disturbance and improved well-being in older persons, according to the study.
When used as prescribed, essential oils rarely cause adverse effects.
There is currently no legislation governing aromatherapists in the United Kingdom, and no licence is required to practise. As a result, it’s critical to choose practitioners and goods wisely.
During pregnancy, insomnia is prevalent, especially in the first and third trimesters.
Hormone fluctuations, nausea, and a greater urge to urinate are just a few of the biological changes that can keep you awake throughout early pregnancy.
You may experience emotional pressures, such as concern about your growing obligations as a mother. You may also be awake due to pain, such as cramping or back discomfort.
To accommodate the new life growing inside you, your body is undergoing several changes, including an active metabolism and a rise in progesterone. It’s also natural for your sleep patterns to shift.
• Maintaining an active lifestyle throughout pregnancy
• Consuming a nutritious diet
• Keeping yourself hydrated
• Maintaining a regular sleeping schedule
• If you feel anxiety, try practising relaxation techniques during the day or taking a warm bath before bedtime
If you want to try a new exercise programme, prescription, or supplement, talk to a doctor first. You’ll want to be sure they’re safe for a pregnant woman.
The good news is that insomnia caused by pregnancy normally passes quickly and has no impact on your baby’s growth.
• Medical conditions
• Social environment
• Psychological or emotional condition
• Sleep history
• Record a sleep journal
• Make a note of when you fall asleep
• Keep track of the times that you wake up repeatedly
• Each day, record what time you wake up.
Your doctor will be able to see your sleep habits if you keep a sleep journal. Medical tests or blood work may be ordered by your doctor to rule out any medical issues that are interfering with your sleep.
When a clinician suspects an underlying sleep condition such as obstructive sleep apnea, a sleep study may be performed not for the diagnosis of insomnia but for confirmation.
Sleep studies can be carried out in two ways. An overnight visit to a sleep facility is one possibility. The second option allows you to study in the comfort of your own home, in your own bed.
Both sleep study techniques require electrodes to be implanted on various parts of your body, including your head.
Children suffering with Insomnia
• Stress
• Medication
• Consuming too much caffeine
• Psychiatric disorders
• Daytime sleepiness or restlessness
• Irritability and mood swings
• Repeated disciplinary issues
• Memory problems and attention deficits
Children’s treatments are frequently the same as adult treatments.
A regular sleep pattern and proper sleep hygiene will help children. Stress reduction and avoiding screen time near bedtime are also beneficial.
Sleeplessness can cause anxiety, while anxiety can cause insomnia. This can lead to a self-fulfilling cycle that eventually leads to chronic sleeplessness.
Short-term anxiety arises when you worry about the same subject over and over again, such as your job or personal connections.
When the problem is remedied, short-term anxiety usually disappears. Your sleep should also return to normal.
Anxiety disorders, such as generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) or panic disorder, can also be identified. Insomnia can be caused by several illnesses in varying degrees.
Anxiety disorders are caused by a variety of factors that aren’t totally understood. Treatment usually lasts a long time and consists of a combination of therapy and drugs.
The same lifestyle and behavioural measures that are recommended for other types of insomnia, such as limiting stressful conversation to the daytime, can help with anxiety-related insomnia.
According to a recent study, insomnia not only increases your chances of developing depression, but sadness can also increase your chances of developing insomnia.
Poor sleep, especially during times of stress, significantly elevated the risk of depression, according to a meta-analysis of 34 research.
Another study discovered that as insomnia progressed and symptoms increased, participants became more depressed.
In certain cases, depression symptoms may come before insomnia.
The good news is that, regardless of whether ailment arises first, the same medicines often assist both sadness and sleeplessness.
The following are the most common treatments:
- Medications
- Therapy
- Lifestyle change
Among the lifestyle adjustments that can be made are:
- Establishing better sleeping habits
- Daytime exercise
- Consuming a healthy diet
Sleep deprivation can have a negative impact on your health. Insomnia can put you at risk for a variety of illnesses, including:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Stroke
- Asthma
- Seizures
- Fatigue
- Weak immune system
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
Insomnia can also:
- Increase your risk for an accident
- Affect your performance at school or work
- Lower your sex drive
- Affect your memory
Insomnia isn’t just an inconvenience or a minor nuisance. It’s a genuine sleep disorder that can be treated.
Consult your doctor if you believe you are suffering from insomnia. They can assist you in determining possible causes and developing a safe and effective treatment strategy based on your medical needs.
Insomnia Treatment & Therapy
Scientific Studies
INSOMNIA
When people with insomnia get up from their sleep, they generally don’t feel refreshed. Fatigue and other symptoms may result as a result of this.
According to the British Sleep Society, insomnia is the most frequent of all sleep disorders (BSS).
In fact, according to the BSS, one-third of all individuals experience insomnia symptoms. Approximately 6 to 10% of all individuals have symptoms severe enough to be diagnosed with insomnia disorder.
Insomnia is defined by the BSS as a sleep condition in which persons have difficulty sleeping or staying asleep. If both of these criteria are met, a clinical diagnosis of insomnia is made:
For a minimum of three months, you must have sleep problems at least three evenings a week.
Major distress or functional issues in a person’s life are caused by sleep problems.
A variety of factors can contribute to short-term or acute insomnia, including:
• Physical pain
• Stress
• Jet lag
• Some medications
• A distressing or traumatic event
• Changes to your sleep habits, like sleeping in a hotel or new home

• Medications that make sleeping difficult, such as arthritis or back pain
• Anxiety or depression, and psychological disorders
• Substance use
• Some medications
• Sleep apnea
• Diabetes
INSOMNIA’S RISK FACTORS
• High-stress levels
• Depression or distress caused by a life event are examples of emotional disorders.
• Low income
• Traveling through various time zones
• Sedentary lifestyle
• Alterations in working hours or night shifts

• A habit of waking up too early in the morning
• Sleep that isn’t really refreshing
• Having difficulty falling or staying asleep
• Mood changes
• Fatigue
• Irritability

• Breathing trouble
• Rapid shallow breathing
• Pressure in your chest, heaviness or pain
• Bluish or grey lips, skin, or nail beds
• Rapid heart rate
• Confusion
• Drowsiness
Insomnia can be treated with both pharmacological and nonpharmaceutical methods.
A doctor can advise you on which therapies are best for you. It’s possible that you’ll have to try a few different therapies before discovering the one that works best for you.
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is recommended as a first-line treatment for chronic insomnia in adults by Mind, a UK mental health advice and support charity.
Training in sleep hygiene may also be recommended. Insomnia can be caused by habits that disrupt sleep. Some of these disruptive behaviours can be changed with sleep hygiene training.
Changes that may be suggested include:
Caffeinated beverages should be avoided near bedtime.
Avoiding exercise in the hours leading up to bedtime
Reducing the amount of time you spend in bed when you aren’t sleeping, such as watching TV or surfing the web on your phone
If you have an underlying psychological or medical issue that is causing your insomnia, seeking therapy for it can help you sleep better.
Find out more about insomnia treatments:

when treating Patients suffering from Insomnia
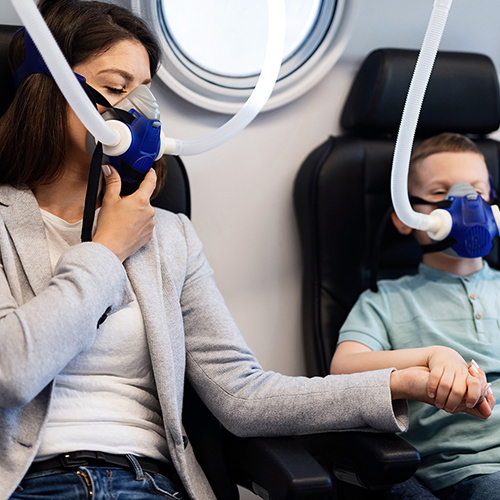

Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
for Insomnia
Ozone Therapy for Insomnia
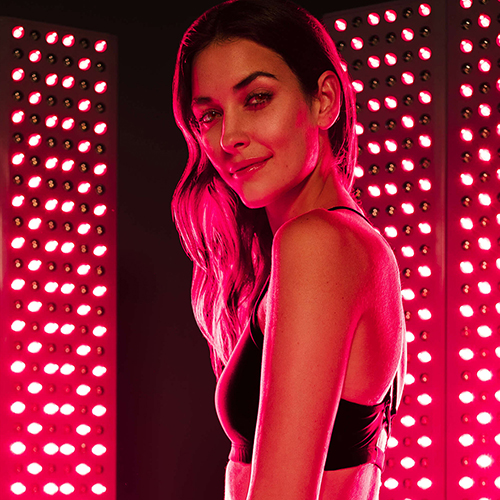

Red Light Therapy
for Insomnia
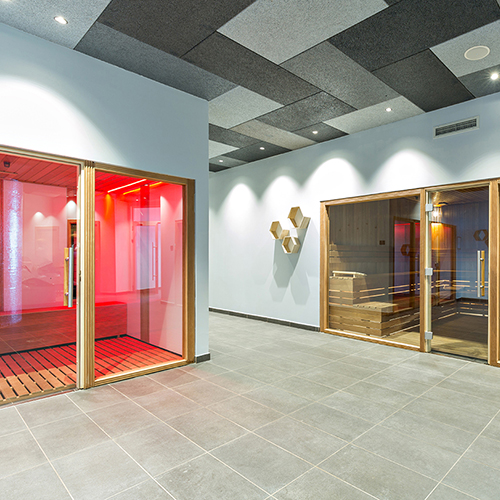

Infrared Sauna Therapy
for Insomnia
Medications are sometimes used to treat insomnia.
An antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine, is an example of an over-the-counter (OTC) drug that can be used for sleep (Benadryl).
Because OTC medications for insomnia might have side effects, especially if used long term, it’s crucial to consult a doctor before using one.
The following are examples of prescription drugs that can be used to treat insomnia:
- Zolpidem (Lunesta)
- Eszopiclone (Ambien)
Before taking any pills or supplements to cure your insomnia, see your doctor.
There could be serious drug interactions or negative effects. Not all “sleep aids” are suitable for everyone.
Find out more about insomnia drugs.
Many cases of insomnia can be effectively managed by making lifestyle modifications or attempting home treatments.
Warm milk, herbal tea, and valerian root are just a few examples of natural sleep aids.
Meditation is a drug-free, natural, and simple approach to treating insomnia.
Meditation, according to a 2015 study, can improve the quality of your sleep and make it easier to fall and remain asleep.
Meditation, according to the Mayo Clinic, can also help with the symptoms of diseases that can cause insomnia. These are some of them:
- Anxiety
- Stress
- Digestive Problems
- Depression
- Pain
Many apps and videos are available to help you practice meditation.
During the sleep cycle, the hormone melatonin is naturally produced. Melatonin pills are frequently used to help people sleep better.
Melatonin has not been proven to benefit adults with insomnia in studies.
There is some evidence that vitamins can help you fall asleep faster, but further research is needed.
Melatonin is generally considered safe for a short length of time, but its long-term safety has yet to be proven.
If you’re thinking about using melatonin, consult a doctor first.
Essential oils are powerful aromatic liquids derived from a range of sources, including:
- Plants
- Flowers
- Trees
People use essential oils to treat a number of ailments by breathing them or massaging them into their skin. Aromatherapy is the name for this type of treatment.
The following essential oils are thought to aid sleep:
- Roman chamomile
- Cedarwood
- Lavender
- Sandalwood
- Neroli, or bitter orange
Aromatherapy was found to be helpful in improving sleep in a review of 12 trials published in 2015.
Lavender was found to be particularly effective in promoting and maintaining sleep in another investigation. A blend of essential oils reduced sleep disturbance and improved well-being in older persons, according to the study.
When used as prescribed, essential oils rarely cause adverse effects.
There is currently no legislation governing aromatherapists in the United Kingdom, and no licence is required to practise. As a result, it’s critical to choose practitioners and goods wisely.
During pregnancy, insomnia is prevalent, especially in the first and third trimesters.
Hormone fluctuations, nausea, and a greater urge to urinate are just a few of the biological changes that can keep you awake throughout early pregnancy.
You may experience emotional pressures, such as concern about your growing obligations as a mother. You may also be awake due to pain, such as cramping or back discomfort.
To accommodate the new life growing inside you, your body is undergoing several changes, including an active metabolism and a rise in progesterone. It’s also natural for your sleep patterns to shift.
• Maintaining an active lifestyle throughout pregnancy
• Consuming a nutritious diet
• Keeping yourself hydrated
• Maintaining a regular sleeping schedule
• If you feel anxiety, try practising relaxation techniques during the day or taking a warm bath before bedtime
If you want to try a new exercise programme, prescription, or supplement, talk to a doctor first. You’ll want to be sure they’re safe for a pregnant woman.
The good news is that insomnia caused by pregnancy normally passes quickly and has no impact on your baby’s growth.
• Medical conditions
• Social environment
• Psychological or emotional condition
• Sleep history
• Record a sleep journal
• Make a note of when you fall asleep
• Keep track of the times that you wake up repeatedly
• Each day, record what time you wake up.
Your doctor will be able to see your sleep habits if you keep a sleep journal. Medical tests or blood work may be ordered by your doctor to rule out any medical issues that are interfering with your sleep.
When a clinician suspects an underlying sleep condition such as obstructive sleep apnea, a sleep study may be performed not for the diagnosis of insomnia but for confirmation.
Sleep studies can be carried out in two ways. An overnight visit to a sleep facility is one possibility. The second option allows you to study in the comfort of your own home, in your own bed.
Both sleep study techniques require electrodes to be implanted on various parts of your body, including your head.
Children suffering with Insomnia
• Stress
• Medication
• Consuming too much caffeine
• Psychiatric disorders
• Daytime sleepiness or restlessness
• Irritability and mood swings
• Repeated disciplinary issues
• Memory problems and attention deficits
Children’s treatments are frequently the same as adult treatments.
A regular sleep pattern and proper sleep hygiene will help children. Stress reduction and avoiding screen time near bedtime are also beneficial.
Sleeplessness can cause anxiety, while anxiety can cause insomnia. This can lead to a self-fulfilling cycle that eventually leads to chronic sleeplessness.
Short-term anxiety arises when you worry about the same subject over and over again, such as your job or personal connections.
When the problem is remedied, short-term anxiety usually disappears. Your sleep should also return to normal.
Anxiety disorders, such as generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) or panic disorder, can also be identified. Insomnia can be caused by several illnesses in varying degrees.
Anxiety disorders are caused by a variety of factors that aren’t totally understood. Treatment usually lasts a long time and consists of a combination of therapy and drugs.
The same lifestyle and behavioural measures that are recommended for other types of insomnia, such as limiting stressful conversation to the daytime, can help with anxiety-related insomnia.
According to a recent study, insomnia not only increases your chances of developing depression, but sadness can also increase your chances of developing insomnia.
Poor sleep, especially during times of stress, significantly elevated the risk of depression, according to a meta-analysis of 34 research.
Another study discovered that as insomnia progressed and symptoms increased, participants became more depressed.
In certain cases, depression symptoms may come before insomnia.
The good news is that, regardless of whether ailment arises first, the same medicines often assist both sadness and sleeplessness.
The following are the most common treatments:
- Medications
- Therapy
- Lifestyle change
Among the lifestyle adjustments that can be made are:
- Establishing better sleeping habits
- Daytime exercise
- Consuming a healthy diet
Sleep deprivation can have a negative impact on your health. Insomnia can put you at risk for a variety of illnesses, including:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Stroke
- Asthma
- Seizures
- Fatigue
- Weak immune system
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
Insomnia can also:
- Increase your risk for an accident
- Affect your performance at school or work
- Lower your sex drive
- Affect your memory
Insomnia isn’t just an inconvenience or a minor nuisance. It’s a genuine sleep disorder that can be treated.
Consult your doctor if you believe you are suffering from insomnia. They can assist you in determining possible causes and developing a safe and effective treatment strategy based on your medical needs.

