What Is Atherosclerosis
and could it affect you?
What Is Atherosclerosis
and could it affect you?
Atherosclerosis (arteriosclerosis) is a potentially fatal disorder in which fatty compounds termed plaques, or atheroma, obstruct arteries.
RISK FACTORS | COMPLICATIONS | PREVENTION |
SUMMARY | CASE STUDIES
Understanding Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the narrowing of arteries due to plaque formation. The blood channels that transport oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body are known as arteries.
Fats, cholesterol, and calcium can build up in your arteries as you get older, forming plaque. Plaque builds up in your arteries, making it difficult for blood to circulate freely. Any artery in your body, including those surrounding your heart, legs, brain, and kidneys, can develop plaque.
It can cause a lack of blood and oxygen throughout your body’s tissues. Plaque fragments can potentially break off and cause a blood clot. Atherosclerosis, if left untreated, can lead to heart attack, stroke, or heart failure, among other things.
Atherosclerosis is a rather prevalent ageing-related disease. This illness can be avoided, and there are numerous effective treatment alternatives.
ARE YOU AWARE?
Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis, which is also known as artery hardening. Although the terms “atherosclerosis” and “arteriosclerosis” are commonly interchanged, they refer to two distinct disorders.
What are some
of the signs and
symptoms?
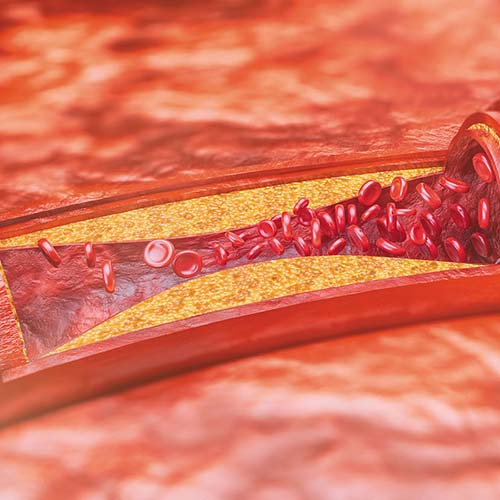
What are some of the signs and symptoms?
The majority of atherosclerosis symptoms don’t appear until a blockage occurs. Symptoms that are common include:
- Angina or chest pain
- Pain in your leg, arm, and anywhere else that has a blocked artery
- Cramping in the buttocks while walking
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Confusion occurs if the blockage affects circulation to your brain
- Loss of motor or sensory function on one side of the body occurs if the blockage affects circulation to your brain
- Muscle weakness in your legs from lack of circulation
It’s also important to be conscious of the signs and symptoms of a heart attack or a stroke. Atherosclerosis can induce both of these conditions, which necessitate rapid medical intervention.
The following are some of the signs and symptoms of a heart attack:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Pain in the shoulders, back, neck, arms, and jaw
- Abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea or vomiting
- A sense of impending doom
The following are some of the signs and symptoms of a stroke:
- Weakness or numbness in the face or limbs
- Trouble speaking
- Trouble understanding speech
- Vision problems
- Loss of balance
- Sudden, severe headache
Both a heart attack and a stroke are life-threatening medical conditions. If you are experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or stroke, call 999 or your local emergency services and go to a hospital’s emergency department as soon as possible.
What causes atherosclerosis?
What causes atherosclerosis?
When plaque builds up in the arteries and they become stiff and inflammatory, blood flow to the rest of the body becomes difficult. This deprives your organs and tissues of the oxygenated blood they require to perform properly.
The following are some of the most common reasons for artery hardening:
High cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy, yellow substance that occurs naturally in the body and is also found in some foods.
Cholesterol levels in the blood can obstruct arteries if they are excessively high. It hardens into a plaque that restricts or prevents blood flow to your heart and other vital organs.
Diet
It is critical to maintain a healthy diet. According to the British Heart Foundation, you should maintain an overall healthy food pattern that emphasises:
- A wide range of fruits and vegetables
- whole grains
- low-fat dairy products
- poultry and fish, without skin
- nuts and legumes
- non-tropical vegetable oils, such as olive or sunflower oil
Other dietary advice:
- Sugar-sweetened beverages, candies, and desserts are among the meals and drinks to avoid. Most women should consume no more than 6 teaspoons or 100 calories of sugar per day, while most males should consume no more than 9 teaspoons or 150 calories per day, according to the BHF.
- Salty meals should be avoided. Aim for a daily sodium intake of no more than 2,300 milligrammes. You should drink no more than 1,500 milligrammes of caffeine each day.
- Trans fats and other harmful fats should be avoided. Saturated fats should be replaced with unsaturated fats, which are healthier. Reduce saturated fat to no more than 5 to 6% of total calories if you need to lower your blood cholesterol. That’s around 13 grammes of saturated fat for someone who consumes 2,000 calories per day.
Ageing
Your heart and blood vessels have to work harder to pump and receive blood as you become older. Your arteries may stiffen and become less elastic, making plaque development more likely.
How is it
diagnosed?
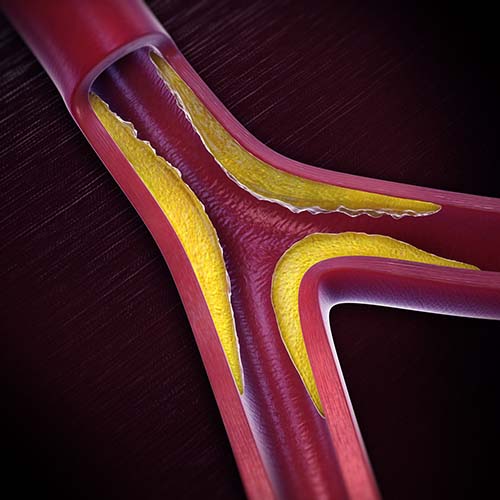
How is it diagnosed?
If you have signs of atherosclerosis, your GP will do a physical examination. They’ll look for the following things:
- A weakened pulse
- An aneurysm, or an abnormal bulging or widening of an artery due to weakness of the arterial wall
- Slow wound healing, which indicates a restricted blood flow
- A bruit, or whooshing sound the blood makes as it travels through the blocked artery
A cardiologist may listen to your heart to hear if any unusual sounds are present. If your GP suspects you have atherosclerosis, they will conduct more tests.
A variety of tests are available, including:
- A blood test to check your cholesterol levels
- A Doppler ultrasound, which uses sound waves to create a picture of the artery that shows if there’s a blockage
- An ankle-brachial index looks for a blockage in your arms or legs by comparing the blood pressure in each limb
- A magnetic resonance angiography or a computed tomography angiography, create pictures of the large arteries in your body
- A cardiac angiogram is a type of chest X-ray that’s taken after your heart arteries are injected with radioactive dye
- An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), measures the electrical activity in your heart to look for any areas of decreased blood flow
- A stress test, or exercise tolerance test, monitors your heart rate and blood pressure while you exercise on a treadmill or stationary bicycle
How is it treated?
How is it treated?
Treatment entails altering your present lifestyle in order to reduce your fat and cholesterol intake. You can boost the health of your heart and blood arteries by exercising more.
As the first line of treatment, your GP may advise you to make lifestyle adjustments. Additional medical treatments, such as drugs or surgery, may be required.
Medications
Medications can help prevent the progression of atherosclerosis.
The following medications are used to treat atherosclerosis:
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs, including statins
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which may lower blood pressure
- Beta-blockers, which “rest” the heart
- Antiplatelet drugs such as aspirin prevent blood from clotting and clogging your arteries
People who have had a history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack or stroke, may benefit from aspirin. If you already have atherosclerosis, an aspirin programme discussed with your doctor may reduce your chance of another health crisis.
Only use aspirin as a preventive drug if your risk of bleeding is low and your risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is high if you have no history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Always consult your doctor before starting an aspirin regimen.
Surgery
Surgery may be required if the symptoms are particularly severe or if muscle or skin tissue is at risk.
The following are some of the operations that may be used to treat atherosclerosis:
- Bypass surgery involves diverting blood around a blocked or narrowed artery using a vessel from another part of your body or a synthetic tube.
- Thrombolytic therapy involves injecting a medication into the affected artery to dissolve a blood clot.
- Angioplasty and percutaneous coronary intervention involve expanding your artery using a catheter and a balloon and sometimes inserting a stent to keep it open.
- Plaque is removed from your arteries using a catheter with a sharp blade at one end, which is known as atherectomy.
- Endarterectomy is a surgical procedure that removes fatty deposits from your arteries.
treatment modalities to treat chronic health issues, including:
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Evidence shows that HBOT is effective in the treatment of PAD and, in addition to helping atherosclerosis, Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can help with wound healing on affected limbs. HBOT works to heal oxygen-deprived tissue by flooding it with increased levels of oxygen, thus promoting cell repair.
Cryotherapy
Recent research on the effect of whole-body cryotherapy on cholesterol levels shows that 10 or more treatments successfully lowered bad cholesterol (LDL) while simultaneously increasing good cholesterol (HDL). Test subjects who received less than 10 treatments did not show improvement in their cholesterol levels.
Ozone therapy
Red Light Therapy
Infrared Sauna therapy

Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Evidence shows that HBOT is effective in the treatment of PAD and, in addition to helping atherosclerosis, Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can help with wound healing on affected limbs. HBOT works to heal oxygen-deprived tissue by flooding it with increased levels of oxygen, thus promoting cell repair.

Cryotherapy
Recent research on the effect of whole-body cryotherapy on cholesterol levels shows that 10 or more treatments successfully lowered bad cholesterol (LDL) while simultaneously increasing good cholesterol (HDL). Test subjects who received less than 10 treatments did not show improvement in their cholesterol levels.

Ozone therapy

Red Light Therapy

Infrared Sauna therapy
Who is at risk for atherosclerosis?
Who is at risk for atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is caused by a variety of reasons. Some risk factors can be altered, while others are beyond our control.
Family history
If you have a family history of atherosclerosis, you may be at risk for artery hardening. This illness, as well as other heart-related issues, can be passed down through the generations.
Lack of exercise
Exercise on a regular basis is beneficial to your heart. It strengthens your heart muscle and promotes the flow of oxygen and blood throughout your body.
Lack of exercise puts you at risk for a variety of health problems, including heart disease.
High blood pressure
High blood pressure might weaken your blood vessels in some locations, causing injury. Cholesterol and other substances in your blood may cause your arteries to become less flexible over time.
Smoking
Tobacco use can cause harm to your blood vessels and heart.
Diabetes
Diabetes patients have a considerably increased risk of coronary artery disease.
What are the complications
associated with atherosclerosis?
What are the complications associated with atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis can cause:
- Heart failure
- Heart attack
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- Stroke
It also causes the following illnesses:
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
Coronary arteries are blood channels that supply oxygen and blood to the heart muscle tissue. Coronary artery disease (CAD) is caused by the hardening of the coronary arteries.
Carotid artery disease
The carotid arteries feed blood to the brain and are located in the neck.
If plaque builds up in the walls of these arteries, they may be jeopardised. The amount of blood and oxygen that reaches your brain’s tissue and cells may be reduced due to a lack of circulation.
Peripheral artery disease
Your arteries carry blood and oxygen to the tissues in your legs, arms, and lower body. Circulation difficulties in these parts of the body can be caused by hardened arteries.
Kidney disease
Your kidneys are supplied with blood via the renal arteries. The kidneys remove waste and excess water from the blood.
Kidney failure can be caused by atherosclerosis of these arteries.
Which lifestyle adjustments
aid in the treatment and
prevention of atherosclerosis?
Which lifestyle adjustments aid in the treatment and prevention of atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis can be prevented and treated with lifestyle changes, especially in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Among the lifestyle adjustments that can be beneficial are:
- Eating a healthy diet that’s low in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Avoiding fatty foods
- Adding fish to your diet twice per week instead of red meat
- Getting at least 75 minutes of vigorous exercise or 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week
- If you’re a smoker quit smoking
- Maintaining a moderate and healthy-for-you weight
- Stress management
- Treating conditions associated with atherosclerosis, such as hypertension, high cholesterol, sleep apnea, obesity, and diabetes
Summary

Summary
Your health may improve as a result of treatment, although it may take some time. Your treatment’s success will be determined by:
- The severity of your condition
- How promptly it was treated
- Whether other organs were affected
The hardening of the arteries is irreversible. Treating the underlying cause and making healthy lifestyle and nutritional adjustments, on the other hand, can help delay or stop the progression.
Consult your GP about making the necessary lifestyle adjustments. They’ll assist you in locating the appropriate medication to help you manage your health and avoid complications.